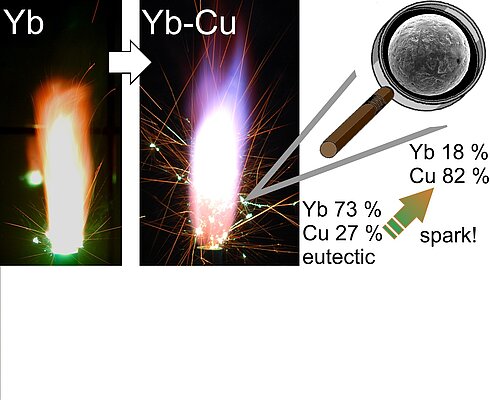
Customizing the Appearance of Sparks with Binary Metal Alloys
Alloys consisting of >65 at. % of a brightly emitting and low-boiling-point metal and a carrier metal allow achieving long-flying deeply colored sparks. Besides the color, branching of sparks is crucial for the visual appearance. Rare-earth...
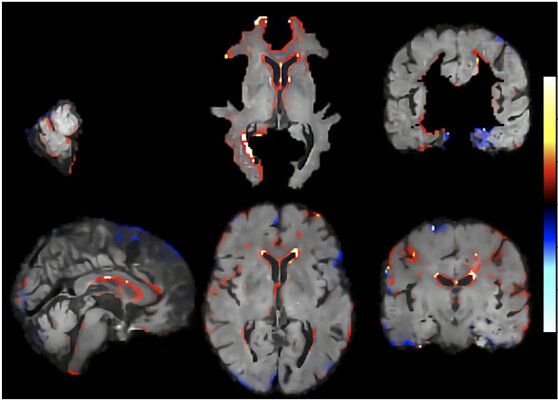
Towards the Interpretability of Deep Learning Models for Human Neuroimaging
Brain-age (BA) estimates based on deep learning are increasingly used as neuroimaging biomarker for brain health; however, the underlying neural features have remained unclear. We combined ensembles of convolutional neural networks with...
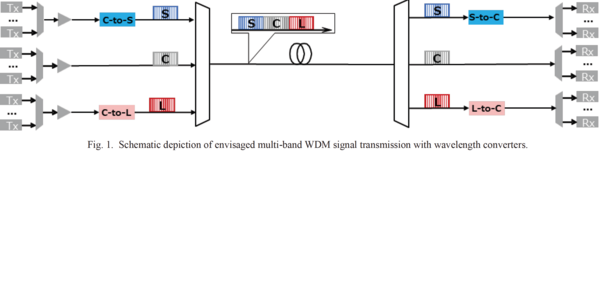
Characterization of Dispersion-Tailored Silicon Strip Waveguide for Wideband Wavelength Conversion
In view of application to wideband wavelength conversion, an SOI waveguide was fabricated and characterized. Conversion of C- band WDM test signals into S- and L- bands in a single waveguide is demonstrated.
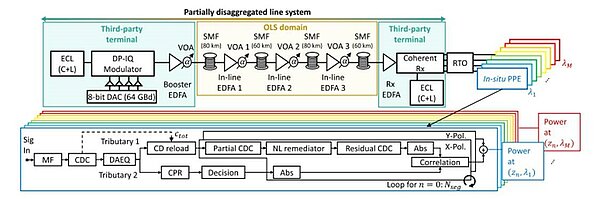
DSP-Based Link Tomography for Amplifier Gain Estimation and Anomaly Detection in C+L-Band Systems
In this work, we propose a spatially-resolved and wavelength-dependent DSP-based monitoring scheme to accurately estimate the spectral gain profile of C+L-band in-line Erbium-doped fiber amplifiers deployed in a 280-km single mode fiber link.
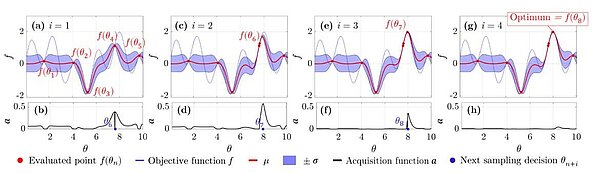
Bayesian Optimization for Nonlinear System Identification and Pre-distortion in Cognitive Transmitters
We present a digital signal processing (DSP) scheme that performs hyperparameter tuning (HT) via Bayesian optimization (BO) to autonomously optimize memory tap distribution of Volterra series and adapt parameters used in the synthetization of a...
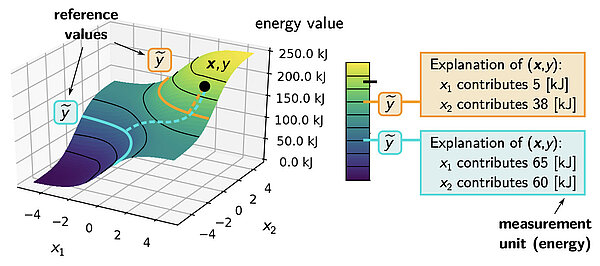
Toward Explainable AI for Regression Models
While such Explainable AI (XAI) techniques have reached significant popularity for classifiers, so far little attention has been devoted to XAI for regression models (XAIR). In this review, we clarify the fundamental conceptual differences of XAI...
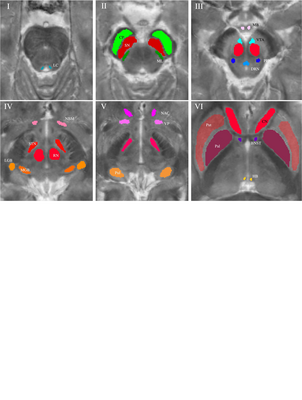
Multiparametric MRI for characterization of the basal ganglia and the midbrain
In this joint work with the University of Heidelberg, German Cancer Research Center, University Hospital of Erlangen we showed that multimodal quantitative MR enabled excellent differentiation of a wide spectrum of subcortical nuclei with...
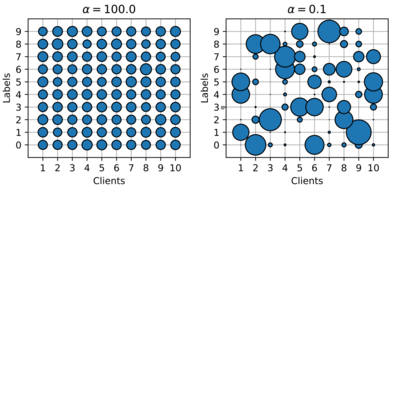
Communication-Efficient Federated Distillation via Soft-Label Quantization and Delta Coding
Communication constraints prevent the wide-spread adoption of Federated Learning systems. In this work, we investigate Federated Distillation (FD) from the perspective of communication efficiency by analyzing the effects of active...
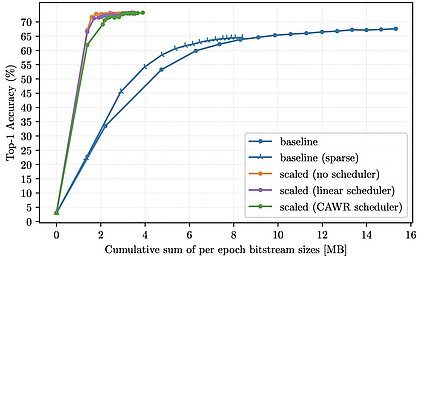
Adaptive Differential Filters for Fast and Communication-Efficient Federated Learning
Federated learning (FL) scenarios inherently generate a large communication overhead by frequently transmitting neural network updates between clients and server. In this work, we propose a new scaling method operating at the granularity of...
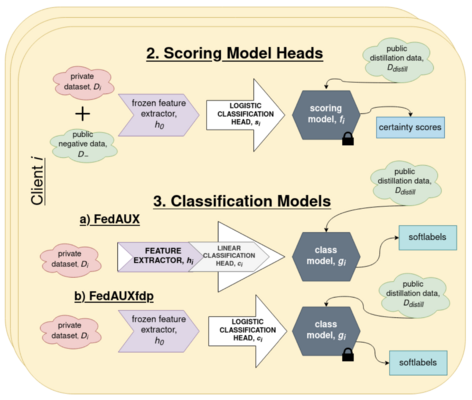
Differentially Private One-Shot Federated Distillation
Federated learning suffers in the case of "non-iid" local datasets, i.e., when the distributions of the clients’ data are heterogeneous. One promising approach to this challenge is the recently proposed method FedAUX, an augmentation of federated...