
Overview
The Fraunhofer Heinrich Hertz Institute develops Time Taggers for quantum key distribution (QKD), where precise timing of individual photons is a key requirement for secure and reliable communication. These in-house, cost-effective time-to-digital converters deliver stable, low-error sub-nanosecond timing performance and are designed for easy integration into existing systems.
The technology is available in two variants. The Time Tagger FMC is designed for FPGA-based, high-end systems and delivers 100 ps resolution with low timing error and high flexibility. The Time Tagger Device is a compact, stand-alone solution offering 160 ps resolution, up to 14 Mdec/s throughput, and simple operation via a standard Ethernet interface. An external clock input enables precise synchronization; otherwise, the internal reference is used.
Both variants support multi-channel event detection and are suitable for demanding timing applications such as QKD, LiDAR, and time-correlated single-photon counting.
Benefits
- Low cost
- Easy integration
- No calibration required
- FMC card available for high-end FPGA systems
Features
- Multiple input channels
- Adjustable threshold and hysteresis
- Ethernet interface (Time Tagger Device)
- Fully customizable interface (Time Tagger FMC)
- Available as a stand-alone measurement device or as a compact FPGA IP core
Variants
| Time Tagger FMC | Time Tagger Device |
|---|---|
| Use with FPGA development platforms | Stand-alone |
| 8 channels | 4 channels |
| One gigabit transceiver per channel | Ethernet connectivity |
| 100 ps bin size | 160 ps bin size |
| Depending on the FPGA development platform | Up to 14 Mdec/s total throughput |

Applications
This technology is available for use in a variety of applications that require precise timing and detection of specific events. These include quantum communication, LiDAR, satellite laser ranging (SLR), time-correlated single-photon counting (TCSPC), and multi-channel scaling (MCS), where the accurate measurement of optical signal arrival times, down to single photons, plays a key role.
Application Examples
Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)
Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)

Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) relies on the HHI Time-Tagger to precisely identify single photons based on their arrival time. Each detection event is timestamped, enabling accurate qubit assignment across different detector channels.
Since photons may take paths of varying lengths, the Time-Tagger’s configurable offsets ensure precise compensation without additional software processing. Flexible settings for thresholds, signal edges, and dead times allow optimal adaptation to different single-photon detectors while effectively suppressing afterpulses and false signals.
The result: highly reliable, high-precision timing performance for advanced QKD systems.
Satellite Laser Ranging (SLR) and Incoherent LiDAR
Satellite Laser Ranging (SLR) and Incoherent LiDAR
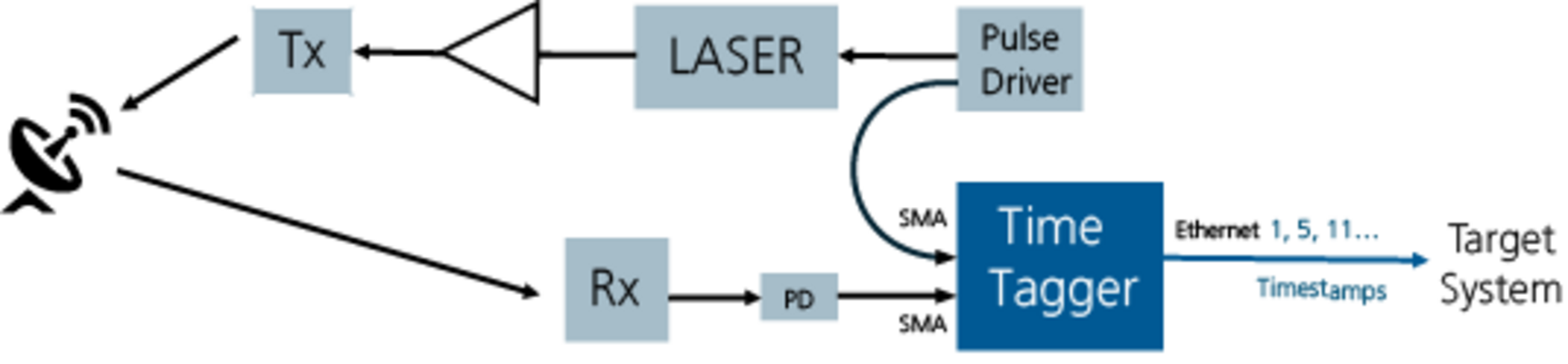
A laser generates short light pulses whose reflections are received by an optical antenna and converted into electrical signals by a photodiode. The Time-Tagger assigns precise timestamps to both the transmitted pulse and the received reflection. The time difference between these timestamps enables distance measurements with an accuracy of about 24 mm.
Configurable offsets and adjustable signal and edge settings ensure easy integration into existing setups and allow precise adaptation to the electrical characteristics of the photodiode and laser driver.

