Spot Size Converters for Enhanced Coupling Efficiency Between Single Mode Fibers and High-Confinement Si3N4 Waveguides
For highly loss-sensitive applications of photonic integrated circuits (PICs), efficient coupling of high-confinement silicon nitride (Si3N4) passive waveguides with active optoelectronic components and standard single mode fibers (SMF) is...
Wavelength Tunable, Polymer-Based Arrayed Waveguide Gratings for Hybrid Integration
We present a hybrid integrated photonic circuit with tunable arrayed waveguide gratings (AWGs) as (DE-)MUX stages for optical modulators for use in parallel convolution processing. The simulated and fabricated AWGs have 16 outputs with 500 GHz...
Gaussian Splatting Decoder for 3D-aware Generative Adversarial Networks
We present a novel approach that combines the high rendering quality of NeRF-based 3D-aware GANs with the flexibility and computational advantages of 3DGS. By training a decoder that maps implicit NeRF representations to explicit 3D Gaussian...
Optimized Detection with Analog Beamforming for Monostatic Integrated Sensing and Communication
This paper presents an optimization framework for analog beamforming in monostatic integrated sensing and communication (ISAC), which maximizes sensing detection under self-interference cancellation via superiorized projections onto convex...
Towards Bridging the Gap between Near and Far-Field Characterizations of the Wireless Channel
Exploring near-field propagation is vital for 6G technologies like intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRS). Unlike far-field models, near-field models offer accuracy critical for applications such as beamforming and multiple-access, enhancing...
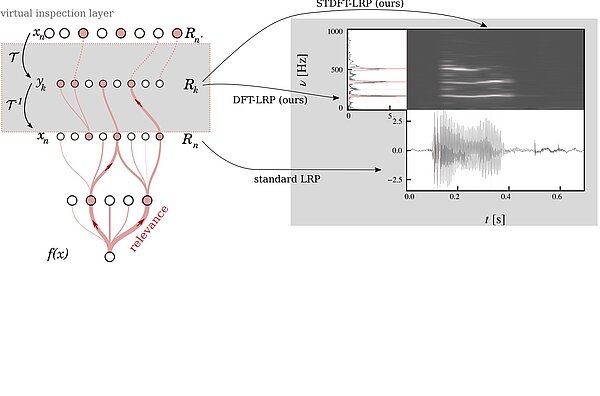
Explainable AI for Time Series via Virtual Inspection Layers
For time series data, where the input itself is often not interpretable, dedicated XAI research is scarce. In this work, we put forward a virtual inspection layer for transforming the time series to an interpretable representation and allows to...
An integrated 800 Gb/s O-band WDM optical transceiver enabled by hybrid InP-Polymer photonic integration
We propose and demonstrate a novel O-band wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) optical transceiver enabled by the hybrid photonic integration of Indium Phosphide (InP) components into a Polymer based photonic motherboard c! alled PolyBoard. The...
Dynamic Exposure Visualization of Air Quality Data with Augmented Reality
This paper introduces a new concept and outlines the implementation of an AR application designed for mobile devices. It can visualize real-time environmental data from various Open Data platforms. The scientific contribution lies in diverse...
Time-bin entanglement at telecom wavelengths from a hybrid photonic integrated circuit
We present a fiber-pigtailed hybrid photonic circuit comprising nonlinear waveguides for photon-pair generation and a polymer interposer reaching 68 dB of pump suppression and photon separation based on a polarizing beam splitter with > 25 dB...
Towards an AI-enabled Connected Industry: AGV Communication and Sensor Measurement Datasets
We present iV2V and iV2i+, two machine-learning datasets for industrial wireless communication. The datasets cover sidelink and cellular communication involving autonomous robots together with localization and sensing data, which can be used to...