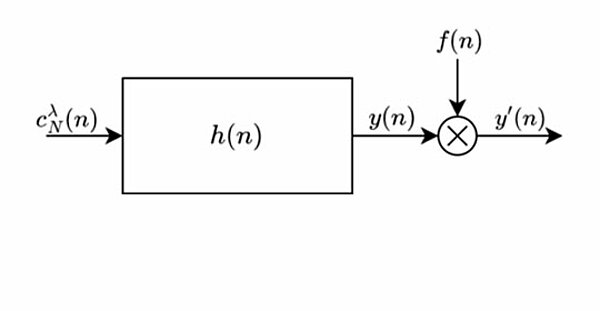
Channel estimation with Zadoff–Chu sequences in the presence of phase errors
Due to their perfect periodic autocorrelation property, Zadoff–Chu sequences are often used as stimulus signals in the measurement of radio channel responses. In this letter, the cross-correlation of a linear shift-invariant system's response to...
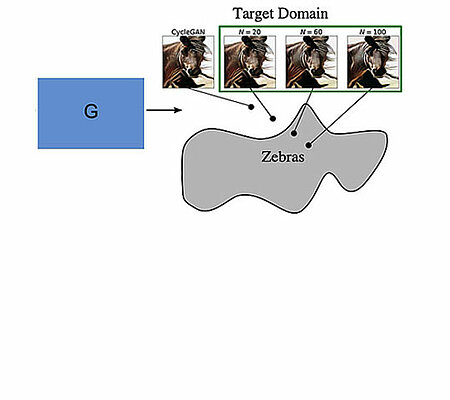
Langevin Cooling for Unsupervised Domain Translation
In this paper, we show that many of such unsuccessful samples in image-to-image translation lie at the fringe—relatively low-density areas of data distribution, where the DNN was not trained very well. To tackle this problem we propose to perform...
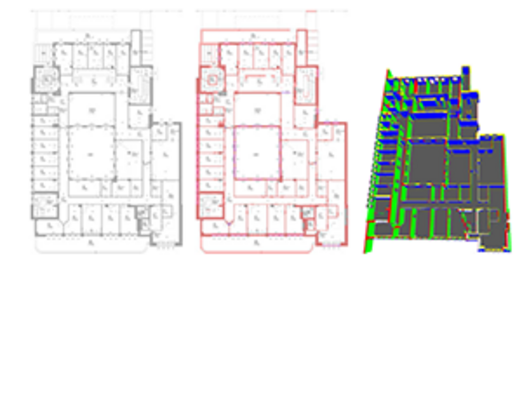
Towards automated digital building model generation from floorplans and on-site images
We propose a system to automatically generate enriched digital models from this data, consisting of two AI modules: one for 3D model reconstruction from 2D plans and one for 6D localization of images taken within a building in the corresponding...
Characterization of C-Band Coherent Receiver Front-ends for Transmission Systems beyond S-C-L-Band
Fraunhofer HHI Researchers investigate in this publication a cost-efficient capacity upgrade of optical transmission systems by the reuse of already deployed single mode fiber. This is enabled by the benefits of other transmission bands, to...
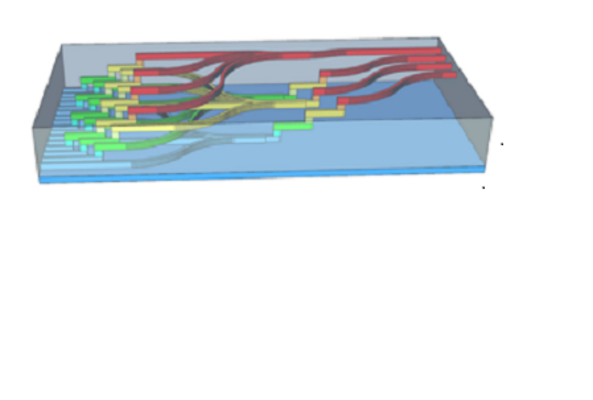
Design and Fabrication of Crossing-free Waveguide Routing Networks using a Multi-layer Polymer-based Photonic Integration Platform
A novel 16x4 crossing-free waveguide routing network on four layers of polymer-based stacked waveguides is presented. The design and fabricated device combine in-plane passive waveguide structures with vertical multimode interference couplers to...
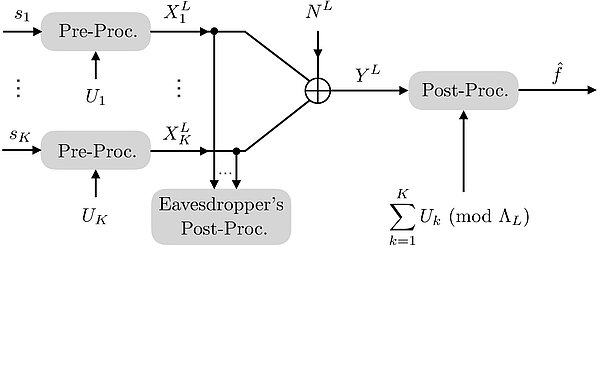
Private and Secure Over-the-Air Multi-Party Communication
Over-the-Air Multi-Party Communication for scalable, private, secure and dependable data aggregation: This novel approach combines lattice coding, Over-the-Air computation and secure Multi-Party Communication to confidentially aggregate analog...
Pre-Training with Fractal Images Facilitates Learned Image Quality Estimation
Current image quality estimation relies on data-driven approaches, however the scarcity of annotated data poses a bottleneck. This paper introduces a novel pre-training approach utilizing synthetic fractal images. The proposed method is tested on...
A Differentiable Gaussian Prototype Layer for Explainable Fruit Segmentation
We introduce a GMM Layer for gradient-based prototype learning. It is used to cluster feature vectors by computing their probabilities for each gaussian and using the soft cluster assignment for prediction. Hence prototypical image regions can be...
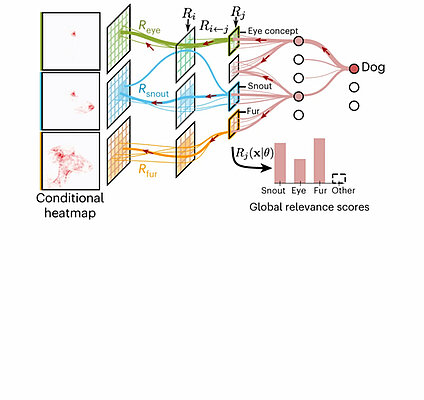
From Attribution Maps to Human-Understandable Explanations through Concept Relevance Propagation
We introduce the Concept Relevance Propagation (CRP) approach, which combines the local and global perspectives and thus allows answering both the ‘where’ and ‘what’ questions for individual predictions. We demonstrate the capability of our...
When it comes to Earth observations in AI for disaster risk reduction, is it feast or famine? A topical review
Given the number of in situ and remote (e.g. radiosonde/satellite) monitoring devices, there is a common perception that there are no limits to the availability of EO for immediate use in such AI-based models. However, a mere fraction of EO is...