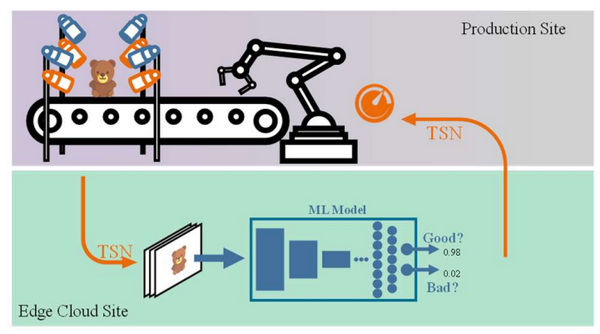
Edge Cloud based Visual Inspection for Automatic Quality Assurance in Production
We present a remote quality assurance use-case in distributed production sites that can be realized with the powerful capabilities of Artificial Intelligence (AI) combined with real-time video streaming systems and high-speed, low-latency...
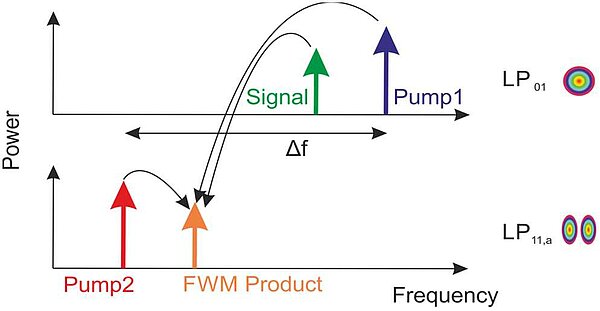
Ultra-Broadband Optical Wavelength-Conversion using Nonlinear Multi-Modal Optical Waveguides
Ultra-Broadband Wavelength Conversion is one of the key issues of future optical networks. The physical background of ultra-broadband optical wavelength conversion in a multi-modal Silicon waveguide and methods to optimize its functionality are...
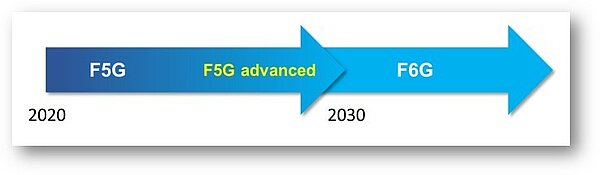
Fixed 5th Generation Advanced and Beyond
One of the overarching goals of the ETSI Industry Specification Group (ISG) F5G on Fifth Generation Fixed Network is to establish a regular rhythm of evolution for the fixed telecommunications network. So far, F5G has published technical...
Towards Trustworthy AI in Dentistry
Medical and dental artificial intelligence (AI) require the trust of both users and recipients of the AI to enhance implementation, acceptability, reach, and maintenance. Standardization is one strategy to generate such trust, with quality...
Federated Learning in Dentistry: Chances and Challenges
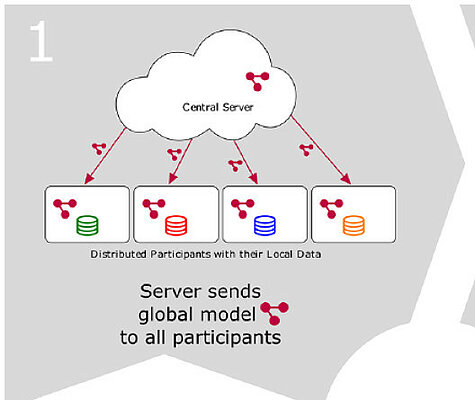
Building performant and robust artificial intelligence (AI)–based applications for dentistry requires large and high-quality data sets. Collaborative efforts are limited as privacy constraints forbid direct sharing across the borders of these...
Optical Generation and Transmission of mmWave Signals in 5G ERA: Experimental Evaluation Paradigm
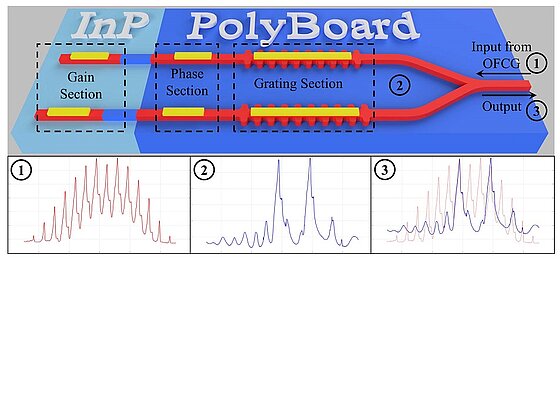
We demonstrate the generation, of a mmWave signal via the injection of an optical frequency comb (OFC) into an integrated tunable dual distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) laser as well as the fiber transmission and the processing of this signal by...
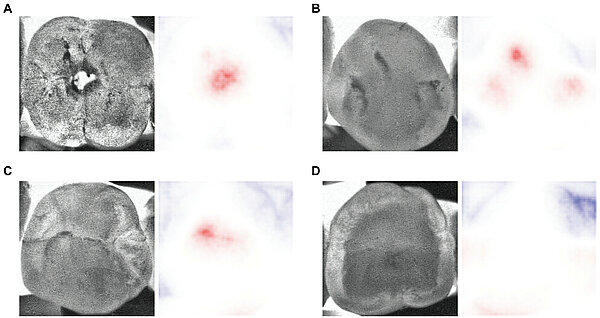
Measurably Stronger Explanation Reliability Via Model Canonization
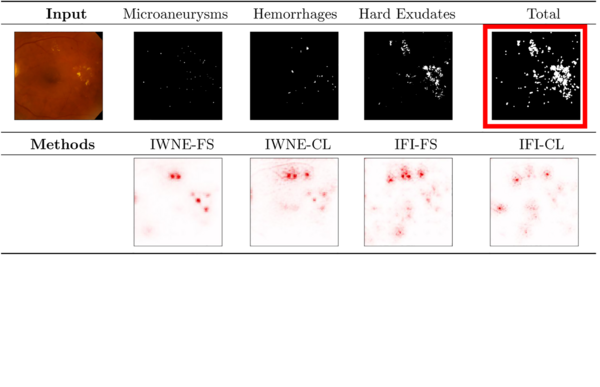
Network canonization has recently been introduced, restructuring a neural network model into a functionally identical equivalent to which established explanation methods can be applied optimally. In this work, we quantitatively verify the...
History Dependent Significance Coding for Incremental Neural Network Compression
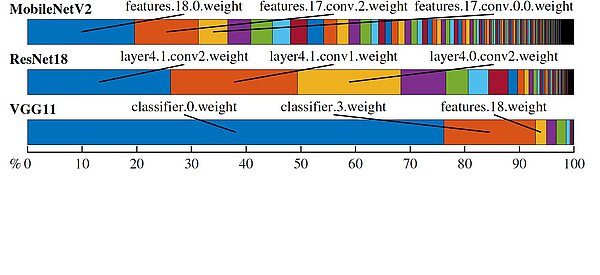
This paper presents an improved probability estimation scheme for the entropy coder of Incremental Neural Network Coding (INNC), which is currently under standardization in ISO/IEC MPEG. Major finding is that the probability of a significant...
To Pretrain or Not? A Systematic Analysis of the Benefits of Pretraining in Diabetic Retinopathy
In this work, we aim to understand what type of pretraining works reliably in practice and what type of pretraining dataset is best suited to achieve good performance in small target dataset size scenarios. Considering diabetic retinopathy...
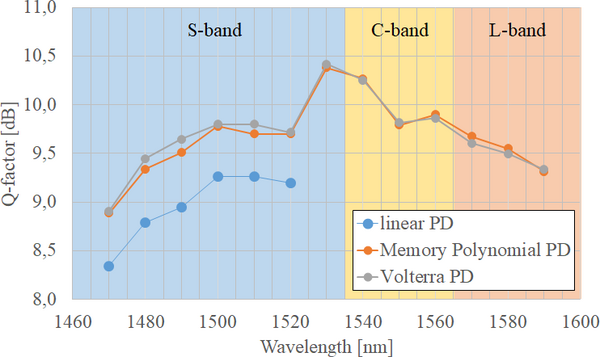
Ultrawideband Systems and Networks: Beyond C+L -Band
In the evolution of optical networks, enhancement of spectral efficiency (SE) enhancement has been the most cost-efficient and thus the main driver for capacity enhancementincrease for decades. As a result, the development of optical transport...