Versatile Video Coding Standard
>ITU-T H.266 | MPEG-I - Part 3 (ISO/IEC 23090-3)
H.266/VVC is the most recent video compression technology to be standardized. It has been developed by the Joint Video Experts Team (JVET) of the ITU-T Visual Coding Experts Group (VCEG) and the ISO/IEC Moving Pictures Experts Group (MPEG). JVET was founded as the Joint Video Exploration Team (on Future Video coding) of ITU-T VCEG and ISO/IEC MPEG in October 2015. After a successful call for proposals [1][2], it transitioned into the Joint Video Experts Team (also abbreviated to JVET) in April 2018 with the task to develop a new video coding standard. The new video coding standard was named Versatile Video Coding (VVC) and has been finalized in July 2020.
The H.266/VVC project timeline can be summarized as follows:
- Exploration Phase
October 2015 - October 2017 - Joint Call for Proposals (CfP)
October 2017 - April 2018 - Development Phase
April 2018 - July 2020 - Final Standard (Version 1)
July 2020
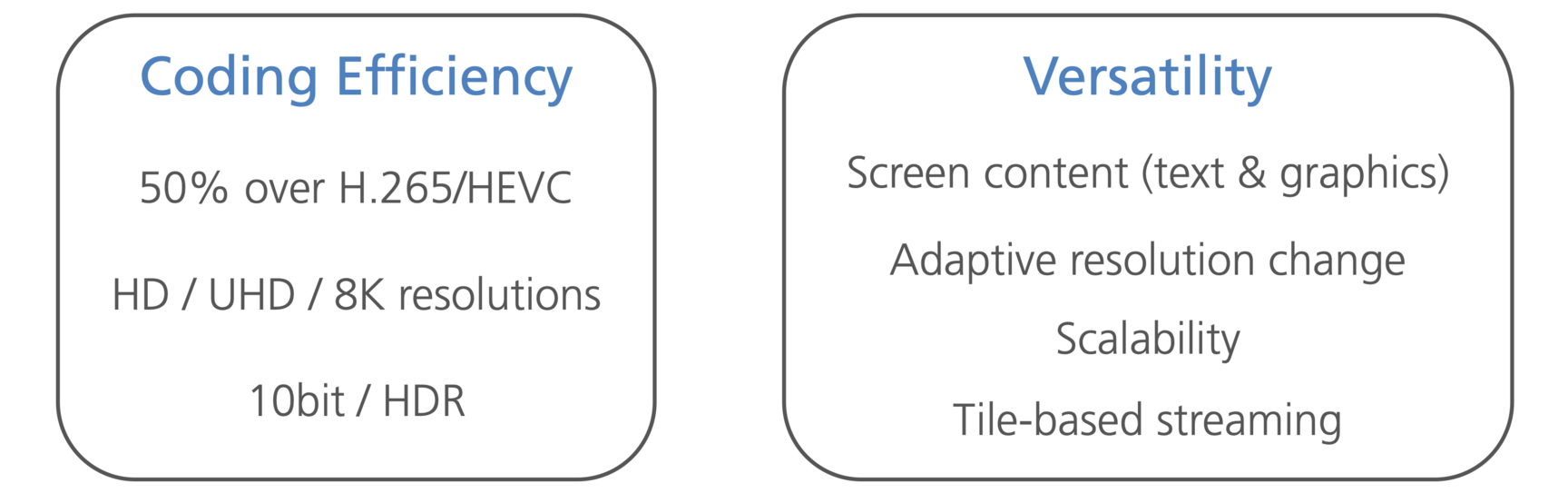
VVC is designed from the ground up to be both efficient and versatile to address today's media needs. This includes:
- 50% bit-rate reduction
over H.265/HEVC, the predecessor standard; - versatility
by efficient coding of a wide range of video content and applications.
VVC includes from version 1 tools specialized for different kinds of content:
- video beyond standard- and high-definition
including high resolution (up to 8K or even larger), high dynamic range (HDR), and wide color gamut; - computer generated or screen content
as occurring in screen sharing and online gaming applications; - immersive content
such as 360-degree video.
NOTE — More information on H.266/VVC can be found on the VVC support site.
Contributions of the Video Communication and Applications Department
The Video Coding Technologies Group contributed several essential coding tools and technologies to the H.266/VVC standard, as listed below. Some of the contributions were developed in cooperation with the Multimedia Communication Group and the Video Coding Systems Group.
In version 1 of H.266/VVC we contributed:
- Partitioning methods
- Transform Coefficient Quantization and Coding
- Machine Learning Based Compression
- Advanced prediction and reconstruction methods
- High-level Syntax and System integrations
- Software Framework for the VVC Test Model (VTM)
Administrative Support
The Video Coding Systems and Video Coding Technologies Groups have been involved in the administration of the JVET standardization in three major ways:
- Benjamin Bross has been appointed as Editor for the JVET project.
- Karsten Sühring has been appointed as Coordinator for the VTM reference software.
- HHI has been chosen to host the VTM Reference Software GitLab repository.
References
- J. Pfaff, H. Schwarz, D. Marpe, B. Bross, S. De-Luxán-Hernández, P. Helle, C. R. Helmrich, T. Hinz, W. Q. Lim, J. Ma, T. Nguyen, J. Rasch, M. Schäfer, M. Siekmann, G. Venugopal, A. Wieckowski, M. Winken, and T. Wiegand, “Video Compression Using Generalized Binary Partitioning and Advanced Techniques for Prediction and Transform Coding,” IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems For Video Technology (TCSVT), 2019. DOI: 10.1109/TCSVT.2019.2945918
- B. Bross et al., “General Video Coding Technology in Responses to the Joint Call for Proposals on Video Compression with Capability beyond HEVC,” IEEE Trans. on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (TCSVT), 2019. DOI: 10.1109/TCSVT.2019.2949619
- B. Bross, J. Chen, S. Liu, Y.-K. Wang, “Versatile Video Coding (Draft 10),” doc. JVET-S2001 of ITU-T/ISO/IEC Joint Video Exploration Team (JVET), 19th meeting by Teleconference, June 2020
- VTM Reference Software