Seeing and Modelling Humans

Gaussian Splatting Decoder for 3D-aware GANs
We present a novel approach that combines the high rendering quality of NeRF-based 3D-aware Generative Adversarial Networks with the flexibility and computational advantages of 3DGS. By training a decoder that maps implicit NeRF representations to explicit 3D Gaussian Splatting attributes, we can integrate the representational diversity and quality of 3D GANs into the ecosystem of 3D Gaussian Splatting. Read more

Multi-view Inversion for 3D-aware Generative Adversarial Networks
We developed a method building on existing state-of-the-art 3D GAN inversion techniques to allow for consistent and simultaneous inversion of multiple views of the same subject. We employ a multi-latent extension to handle inconsistencies present in dynamic face videos to re-synthesize consistent 3D representations from the sequence. Read more
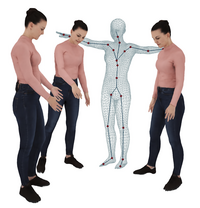
Neural Human Modelling and Animation
We train deep neural networks on high resoution volumetric video data of an actor in order to learn a generative model for the synthesis of new motion sequences with highly realistic shape and appearance. We use a-priori knowledge in form of a statistical human model in order to guide the learning process. Besides explicit representations, we also explore representations like NeRF for human representation and animation. Read more
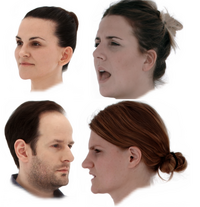
Neural Head Modelling
We present a framework for the automatic creation of animatable human face models from calibrated multi-view data. Based on captured multi-view video footage, we learn a compact latent representation of facial expressions by training a variational auto-encoder on textured mesh sequences. Read more
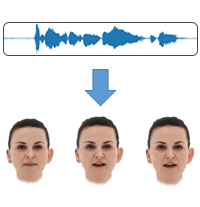
Speech-driven Facial Animation
We have developed various speech/text-driven animation methods based on viseme input such that our avatars can be driven by either speech or text. Read more
Video-driven Face Animation
Video-driven animation transfers the facial expression from the video of a source actor to an animatable face model or avatar. We developed a new video-driven animation approach in order to drive our neural head model based on a pre-trained expression analysis network that provides subject-independent expression information.

Deep Fake Detection
We conduct research on both the generation as well as the detection of Deepfake content. In case of the former, we focus our research on the development of novel model architectures, aiming for an increase in percieved quality and photorealism of the fakes. Moreover, we study the models generalization to arbitrary identities. Read more.

From Volumetric Video To Animation
We present a pipeline for creating high-quality animatable volumetric video content. Key features are the supplementation of captured data with semantics and animation properties and leveraging of geometry- and video-based animation methods. We suggest a three-tiered solution: modeling low-resolution features in the geometry, overlying video-based textures to capture subtle movements, and synthesizing camplex features using an autoencoder-based approach. Read more
Scenes, Structure and Motion

Robust Keypoints
We introduce RIPE, an innovative weakly-supervised training framework based on Reinforcement Learning. RIPE demonstrates that keypoint detection and description can be learned using only image pairs. A positively labeled image pair contains enough implicit information to guide the learning process. Leveraging the epipolar constraint prevents collapse to trivial solutions and provides a strong reward signal. Read more

Compact 3D Scene Representation
We introduce a compact scene representation organizing the parameters of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) into a 2D grid with local homogeneity, ensuring a drastic reduction in storage requirements without compromising visual quality during rendering. Read more

6D Camera Localization in Unseen Environments
We present SPVLoc, a global indoor localization method that accurately determines the six-dimensional (6D) camera pose of a query image and requires minimal scene-specific prior knowledge and no scene-specific training. Read more
AI-Based Building Digitalization
We employ AI, specifically deep neural networks, to automate and streamline the manual processes involved in building digitalization. This enhances efficiency in tasks such as gathering information from diverse sources for monitoring and automation within the construction industry. Read more

Event-Based Vision
Event cameras are novel imaging sensors that respond to local changes in brightness and send an asynchronous strame of change detections (events) per pixel. Hence, each pixel operates independently and asynchronously, leading to low latency, high dynamic range and low data. This means, that new methods have to be developed for this type of data. We develop event-based solutions to different Computer Vision problems and applications.

Tree and Plant Modeling
Image-based plant reconstruction and modeling is an important aspect of digitalization. We address the acquisition, reconstruction and image-based modeling of plants with classical Computer Vision approaches, modern AI technology and procedural methods from Computer Graphics. Read more

Deep 6 DoF Object Detection and Tracking
The display of local assistance information in augmented reality (AR) systems to support assembly tasks requires precise object detection and registration. We present an optimized deep neural network for 6-DoF pose estimation of multiple different objects in one pass. A pixel-wise object segmentation placed in the middle part of the network provides the input to control a feature recognition module. Our pipeline combines global pose estimation with a precise local real-time registration algorithm and solely synthetic images are used for training.
Computational Imaging and Video
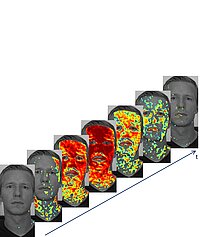
Video-Based Bloodflow Analysis
The extraction of heart rate and other vital parameters from video recordings of a person has attracted much attention over the last years. In our research we examine the time differences between distinct spatial regions using remote photoplethysmography (rPPG) in order to extract the blood flow path through human skin tissue in the neck and face. Our generated blood flow path visualization corresponds to the physiologically defined path in the human body. Read more
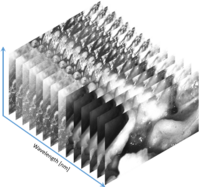
Hyperspectral Imaging
Hyperspectral imaging records images of very many, closely spaced wavelengths, ranging from wavelengths in the ultraviolet to the long-wave infrared with applications in medicine, industrial imaging or agriculture. Reflectance characteristics can be used to derive information in the different wavelengths can be used to derive information on materials in industrial imaging, vegetation and plant health status in agriculture, or tissue characteristics in medicine. We develop capturing, calibration and data analysis techniques for HSI imaging. Read more
Learning and Inference

Anomaly Detection and Analysis
We develop deep learning based methods for the automatic detection and analysis of anomalies in images with a limited amount of training data. For example, we are analyzing and defining different types of damages that can be present in big structures and using methods based on deep learning to detect and localize them in images taken by unmanned vehicles. Some of the problems arising in this task are the unclear definition of what constitutes a damage or its exact extension, the difficulty of obtaining quality data and labeling it, the consequent lack of abundant data for training and the great variability of appearance of the targets to be detected, including the underrepresentation of some particular types. Read more
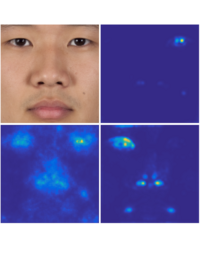
Deep Detection of Face Morphing Attacks
Facial recognition systems can easily be tricked such that they authenticate two different individuals with the same tampered reference image. We develop methods for fully automatic generation of this kind of tampered face images (face morphs) as well as methods to detected face morphs. Our face morph detection methods are based on semantic image content like highlights in the eyes or the shape and appearance of facial features. Read more
Augmented and Mixed Reality

Event-based Structured Light for Spatial AR
We present a method to estimate depth with a stereo system of a small laser projector and an event camera. We achieve real-time performance on a laptop CPU for spatial AR. Read more
Tracking for Projector-Camera Systems
We enable dynamic projection mapping on 3d objects to augment envrinments with interactive additional information. Our method establishes a distortion free projection by first analyzing and then correcting the distortion of the projection in a closed loop. For this purpose, an optical flow-based model is extended to the geometry of a projector-camera unit. Adaptive edge images arer used in order to reach a high invariande to illumination changes. Read more
Older Research Projects
For a list of previous research projects, see here.