Diffuse-scattering-informed Geometric Channel Modeling for THz Wireless Communications Systems
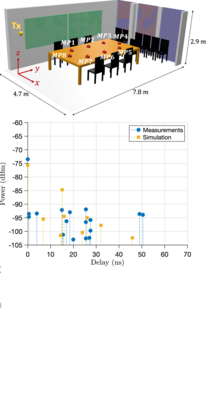
This paper validates an in-house three-dimensional ray-launching (3D-RL) algorithm with a channel sounder measurement campaign that has been performed in a typical indoor environment at 300 GHz.
A hybrid photonic integrated signal source with > 1.5 THz continuous tunability and < 0.25 GHz accuracy for mmW/THz applications
We present a hybrid photonic integrated mmW/THz signal source, which comprises two tunable lasers and on-chip wavelength meters. The continuous wavelength tunability of a single laser is over 12 nm (1.5 THz), and the wavelength meter accuracy is...
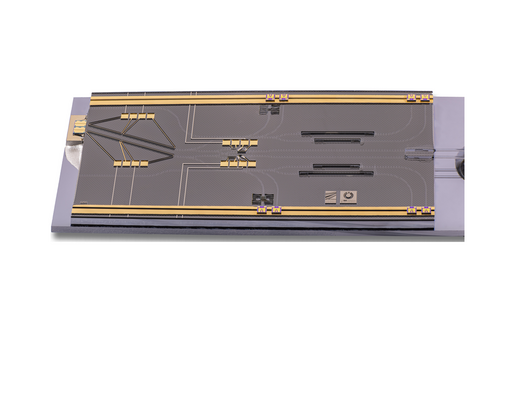
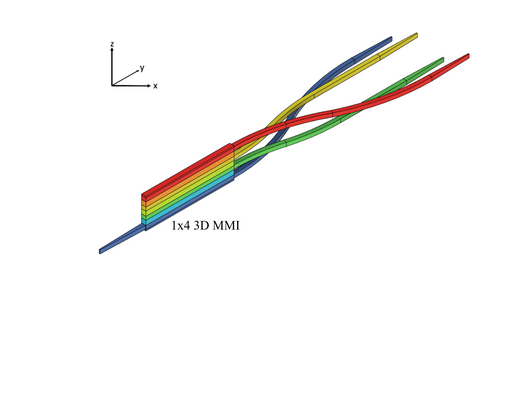
1x4 Vertical Power Splitter/Combiner: A Basic Building Block for Complex 3D Waveguide Routing Networks
A novel polymer-based 1x4 vertical multimode interference (MMI) coupler for 3D photonics is presented. It connects four vertically stacked waveguide layers with a spacing of 21.6 µm. The functionality is demonstrated on a fabricated device.
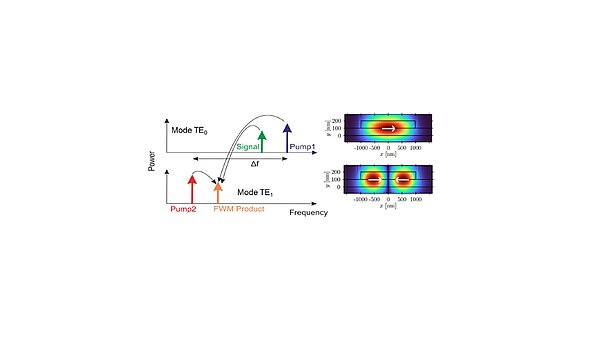
Optimization of Ultra-Broadband Optical Wavelength Conversion in Nonlinear Multi-Modal Silicon-On-Insulator Waveguides
Ultra-broadband wavelength conversion is identified as one of the key issues in future high capacity, flexible optical networks. In this contribution, methods to optimize the design of a multi-modal high-nonlinear SOI waveguide to achieve...
Eight-channel SiNx microring–resonator based photonic biosensor for label-free fluid analysis in the optical C-band
A lab-on-a-chip multichannel sensing platform for biomedical analysis based on optical silicon nitride (SiNx) mi- croring-resonators (MRR) was established. The resonators were surface functionalized and finally combined with a microfluidic...
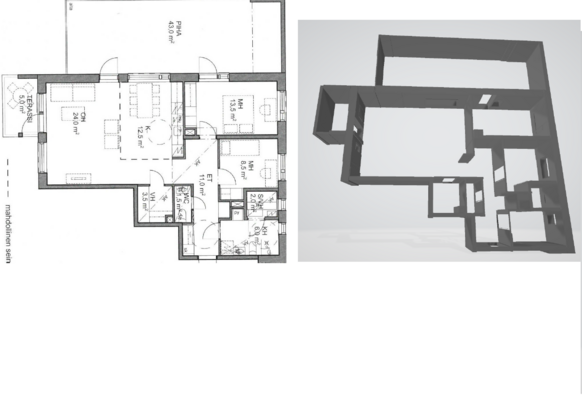
Automatic Reconstruction of Semantic 3D Models from 2D Floor Plans
Digitalization of existing buildings and the creation of 3D BIM models is crucial for many tasks. Of particular importance are floor plans, which contain information about building layouts and are vital for construction, maintenance or...
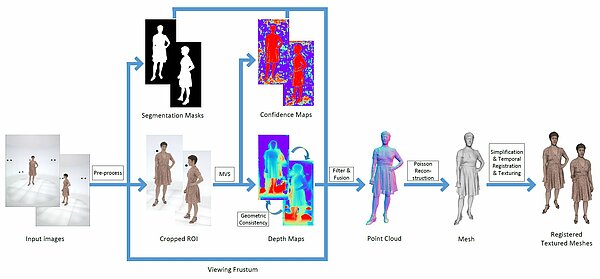
Accurate human body reconstruction for volumetric video
In this work, we enhance a professional end-to-end volumetric video production pipeline to achieve high-fidelity human body reconstruction using only passive cameras.We introduce and optimize deep learning based multi-view stereo networks for...
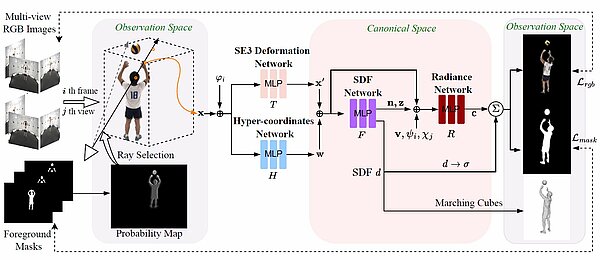
Dynamic Multi-View Scene Reconstruction Using Neural Implicit Surface
In this paper, we propose a template-free method to reconstruct surface geometry and appearance using neural implicit representations from multi-view videos. We leverage topology-aware deformation and the signed distance field to learn complex...
Preserving Memories of Contemporary Witnesses Using Volumetric Video
Oliver Schreer, Peter Eisert, Ingo Feldmann, Anna Hilsmann, Sylvain Renault, Marcus Zepp, Wieland Morgenstern, Rodrigo Mauricio Diaz Fernandez, Markus Worchel
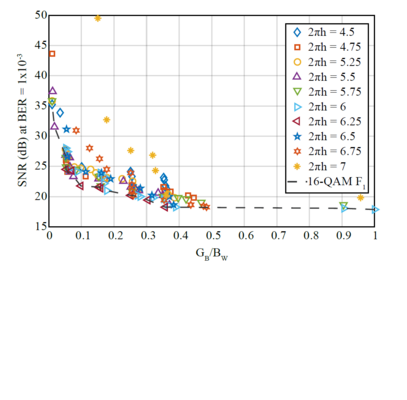
Increasing the power and spectral efficiencies of an OFDM-based VLC system through multi-objective optimization
In order to minimize power usage and maximize spectral efficiency in visible light communication (VLC), we use a multi-objective optimization algorithm and compare DC-biased optical OFDM (DCO-OFDM) with constant envelope OFDM (CE-OFDM)...